Reading List on Britain and the Middle East
History of English
This page is a short history of the origins and development of the English language language
The history of the English really started with the arrival of three Germanic tribes who invaded Britain during the 5th century AD. These tribes, the Angles, the Saxons and the Jutes, crossed the North Sea from what today is Denmark and northern Deutschland. At that time the inhabitants of Britain spoke a Celtic language. Merely most of the Celtic speakers were pushed west and n by the invaders - mainly into what is now Wales, Scotland and Ireland. The Angles came from "Englaland" [sic] and their language was called "Englisc" - from which the words "England" and "English" are derived.
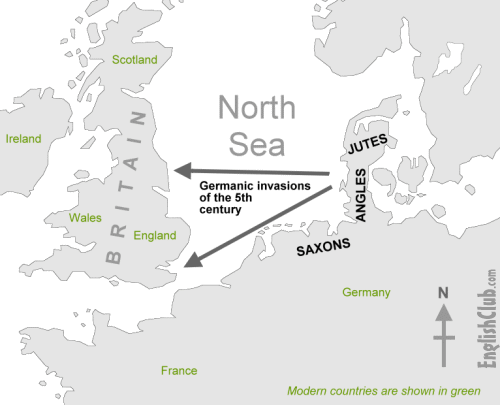
Germanic invaders entered United kingdom on the east and south coasts in the 5th century
One-time English (450-1100 Advertisement)
The invading Germanic tribes spoke similar languages, which in United kingdom adult into what nosotros at present phone call Onetime English. Old English did not audio or look like English language today. Native English speakers at present would have bang-up difficulty understanding Onetime English. Nevertheless, about half of the virtually commonly used words in Modernistic English accept Old English language roots. The words exist, strong and water, for example, derive from Erstwhile English. Old English was spoken until effectually 1100.

Role of Beowulf, a poem written in Sometime English (public domain)
Centre English language (1100-1500)
In 1066 William the Conqueror, the Duke of Normandy (part of mod France), invaded and conquered England. The new conquerors (called the Normans) brought with them a kind of French, which became the language of the Royal Court, and the ruling and business organization classes. For a period in that location was a kind of linguistic grade sectionalisation, where the lower classes spoke English and the upper classes spoke French. In the 14th century English became dominant in Britain again, but with many French words added. This language is called Middle English. Information technology was the language of the neat poet Chaucer (c1340-1400), but it would even so be hard for native English speakers to sympathize today.

An instance of Middle English by Chaucer (public domain)
Modernistic English language
Early Modern English (1500-1800)
Towards the end of Center English, a sudden and distinct modify in pronunciation (the Great Vowel Shift) started, with vowels being pronounced shorter and shorter. From the 16th century the British had contact with many peoples from around the earth.
This, and the Renaissance of Classical learning, meant that many new words and phrases entered the linguistic communication. The invention of press likewise meant that there was now a common language in print. Books became cheaper and more people learned to read. Printing too brought standardization to English. Spelling and grammar became fixed, and the dialect of London, where well-nigh publishing houses were, became the standard. In 1604 the first English dictionary was published.

Lines from Hamlet, written in Early on Mod English by Shakespeare (public domain)
Belatedly Mod English (1800-Present)
The primary departure between Early on Modern English and Late Mod English language is vocabulary. Late Modern English has many more words, arising from two primary factors: firstly, the Industrial Revolution and engineering created a demand for new words; secondly, the British Empire at its pinnacle covered one quarter of the earth'southward surface, and the English language adopted strange words from many countries.
Varieties of English language
From around 1600, the English language colonization of North America resulted in the creation of a distinct American diversity of English. Some English pronunciations and words "froze" when they reached America. In some ways, American English is more like the English of Shakespeare than modern British English is. Some expressions that the British telephone call "Americanisms" are in fact original British expressions that were preserved in the colonies while lost for a fourth dimension in Britain (for example trash for rubbish, loan equally a verb instead of lend, and autumn for fall; another case, frame-up, was re-imported into Britain through Hollywood gangster movies). Spanish too had an influence on American English language (and later on British English), with words like canyon, ranch, stampede and vigilante being examples of Spanish words that entered English through the settlement of the American West. French words (through Louisiana) and West African words (through the slave trade) also influenced American English (and so, to an extent, British English language).
Today, American English language is especially influential, due to the Us's authorisation of movie theatre, telly, popular music, merchandise and technology (including the Cyberspace). Just there are many other varieties of English language around the world, including for instance Australian English, New Zealand English, Canadian English, Due south African English, Indian English and Caribbean area English language.
The Germanic Family of Languages
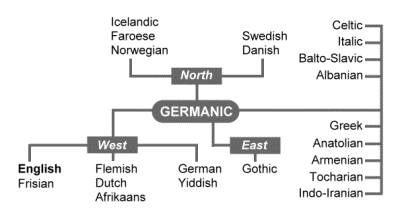
English language is a fellow member of the Germanic family of languages. Germanic is a branch of the Indo-European language family unit.
| A brief chronology of English language | ||
|---|---|---|
| 55 BC | Roman invasion of Britain by Julius Caesar | Local inhabitants speak Celtish |
| AD 43 | Roman invasion and occupation. Offset of Roman rule of Britain | |
| 436 | Roman withdrawal from U.k. complete | |
| 449 | Settlement of Britain past Germanic invaders begins | |
| 450-480 | Earliest known Old English inscriptions | Old English |
| 1066 | William the Conquistador, Duke of Normandy, invades and conquers England | |
| c1150 | Earliest surviving manuscripts in Middle English | Middle English language |
| 1348 | English language replaces Latin as the language of instruction in most schools | |
| 1362 | English replaces French as the linguistic communication of law. English is used in Parliament for the first fourth dimension | |
| c1388 | Chaucer starts writing The Canterbury Tales | |
| c1400 | The Great Vowel Shift begins | |
| 1476 | William Caxton establishes the start English printing press | Early Modern English |
| 1564 | Shakespeare is born | |
| 1604 | Table Alphabeticall, the kickoff English language lexicon, is published | |
| 1607 | The beginning permanent English settlement in the New Globe (Jamestown) is established | |
| 1616 | Shakespeare dies | |
| 1623 | Shakespeare'due south First Folio is published | |
| 1702 | The first daily English language-language paper, The Daily Courant, is published in London | |
| 1755 | Samuel Johnson publishes his English lexicon | |
| 1776 | Thomas Jefferson writes the American Declaration of Independence | |
| 1782 | Britain abandons its colonies in what is after to become the U.s. | |
| 1828 | Webster publishes his American English language dictionary | Belatedly Modern English |
| 1922 | The British Dissemination Corporation is founded | |
| 1928 | The Oxford English language Lexicon is published | |
Updated 2019
Source: https://www.englishclub.com/history-of-english/
0 Response to "Reading List on Britain and the Middle East"
Post a Comment